本文为作者原创文章,转载请注明出处。
模型学习
对每个刚接触XGBoost的同学,强烈建议先多读几遍这个文档:https://xgboost.readthedocs.io/en/latest//model.html。
安装
参考【3】
下载源码
1
git clone --recursive https://github.com/dmlc/xgboost
记得加
--recursive参数,这个仓库依赖了其他仓库编译
1
cd xgboost; cp make/minimum.mk ./config.mk; make -j4
安装Python包
1
cd python-package; sudo python setup.py install
特征映射
我们是以矩阵的形式将数据输入XGBoost模型,而这个矩阵是没有记录特征的名字。而在具体地数据分析中,我们必须知道每个特征对应的含义。这个时候就需要用到feature map文件了。
它的格式可以从这里查看:https://github.com/dmlc/xgboost/tree/master/demo/binary_classification#dump-model
Format of featmap.txt: \n:
- Feature id must be from 0 to number of features, in sorted order.
- i means this feature is binary indicator feature
- q means this feature is a quantitative value, such as age, time, can be missing
- int means this feature is integer value (when int is hinted, the decision boundary will be integer)
XGBoost的作者说了,feature map在训练的时候不会用到。
feature map was provided as a hint for what type the feature is. Such hint was not included during xgboost learning, so that was why a fmap needs to be passed in.
来自:https://github.com/dmlc/xgboost/issues/256#issuecomment-95791921
通过plot_importances函数,可以画出特征的重要性。查看plot_importances: https://github.com/dmlc/xgboost/blob/master/python-package/xgboost/plotting.py
这个方法的缺点是不支持特征映射,不过把源代码copy出来,稍微改一下就能支持啦。
代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108# 添加一个fmap参数
def plot_importance(booster, ax=None, height=0.2,
xlim=None, ylim=None, title='Feature importance',
xlabel='F score', ylabel='Features',
importance_type='weight', max_num_features=None,
fmap=None,
grid=True, show_values=True, **kwargs):
"""Plot importance based on fitted trees.
Parameters
----------
booster : Booster, XGBModel or dict
Booster or XGBModel instance, or dict taken by Booster.get_fscore()
ax : matplotlib Axes, default None
Target axes instance. If None, new figure and axes will be created.
importance_type : str, default "weight"
How the importance is calculated: either "weight", "gain", or "cover"
"weight" is the number of times a feature appears in a tree
"gain" is the average gain of splits which use the feature
"cover" is the average coverage of splits which use the feature
where coverage is defined as the number of samples affected by the split
max_num_features : int, default None
Maximum number of top features displayed on plot. If None, all features will be displayed.
height : float, default 0.2
Bar height, passed to ax.barh()
xlim : tuple, default None
Tuple passed to axes.xlim()
ylim : tuple, default None
Tuple passed to axes.ylim()
title : str, default "Feature importance"
Axes title. To disable, pass None.
xlabel : str, default "F score"
X axis title label. To disable, pass None.
ylabel : str, default "Features"
Y axis title label. To disable, pass None.
show_values : bool, default True
Show values on plot. To disable, pass False.
kwargs :
Other keywords passed to ax.barh()
Returns
-------
ax : matplotlib Axes
"""
# TODO: move this to compat.py
try:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
except ImportError:
raise ImportError('You must install matplotlib to plot importance')
if isinstance(booster, XGBModel):
importance = booster.get_booster().get_score(importance_type=importance_type, fmap=fmap)
elif isinstance(booster, Booster):
importance = booster.get_score(importance_type=importance_type, fmap=fmap)
elif isinstance(booster, dict):
importance = booster
else:
raise ValueError('tree must be Booster, XGBModel or dict instance')
if len(importance) == 0:
raise ValueError('Booster.get_score() results in empty')
tuples = [(k, importance[k]) for k in importance]
if max_num_features is not None:
tuples = sorted(tuples, key=lambda x: x[1])[-max_num_features:]
else:
tuples = sorted(tuples, key=lambda x: x[1])
labels, values = zip(*tuples)
if ax is None:
_, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1)
ylocs = np.arange(len(values))
ax.barh(ylocs, values, align='center', height=height, **kwargs)
if show_values is True:
for x, y in zip(values, ylocs):
ax.text(x + 1, y, x, va='center')
ax.set_yticks(ylocs)
ax.set_yticklabels(labels)
if xlim is not None:
if not isinstance(xlim, tuple) or len(xlim) != 2:
raise ValueError('xlim must be a tuple of 2 elements')
else:
xlim = (0, max(values) * 1.1)
ax.set_xlim(xlim)
if ylim is not None:
if not isinstance(ylim, tuple) or len(ylim) != 2:
raise ValueError('ylim must be a tuple of 2 elements')
else:
ylim = (-1, len(values))
ax.set_ylim(ylim)
if title is not None:
ax.set_title(title)
if xlabel is not None:
ax.set_xlabel(xlabel)
if ylabel is not None:
ax.set_ylabel(ylabel)
ax.grid(grid)
return ax
plot_importance(bst, fmap='data/featmap.txt')
plt.tight_layout() # 解决feature名字太长,被遮住的问题。
plt.gcf().savefig('images/importances.png')
可视化
参考【1】1
plt.gcf().set_size_inches(150, 150)
需要安装graphviz1
brew install graphviz
1 | pip install graphviz |
1 | # plot decision tree |
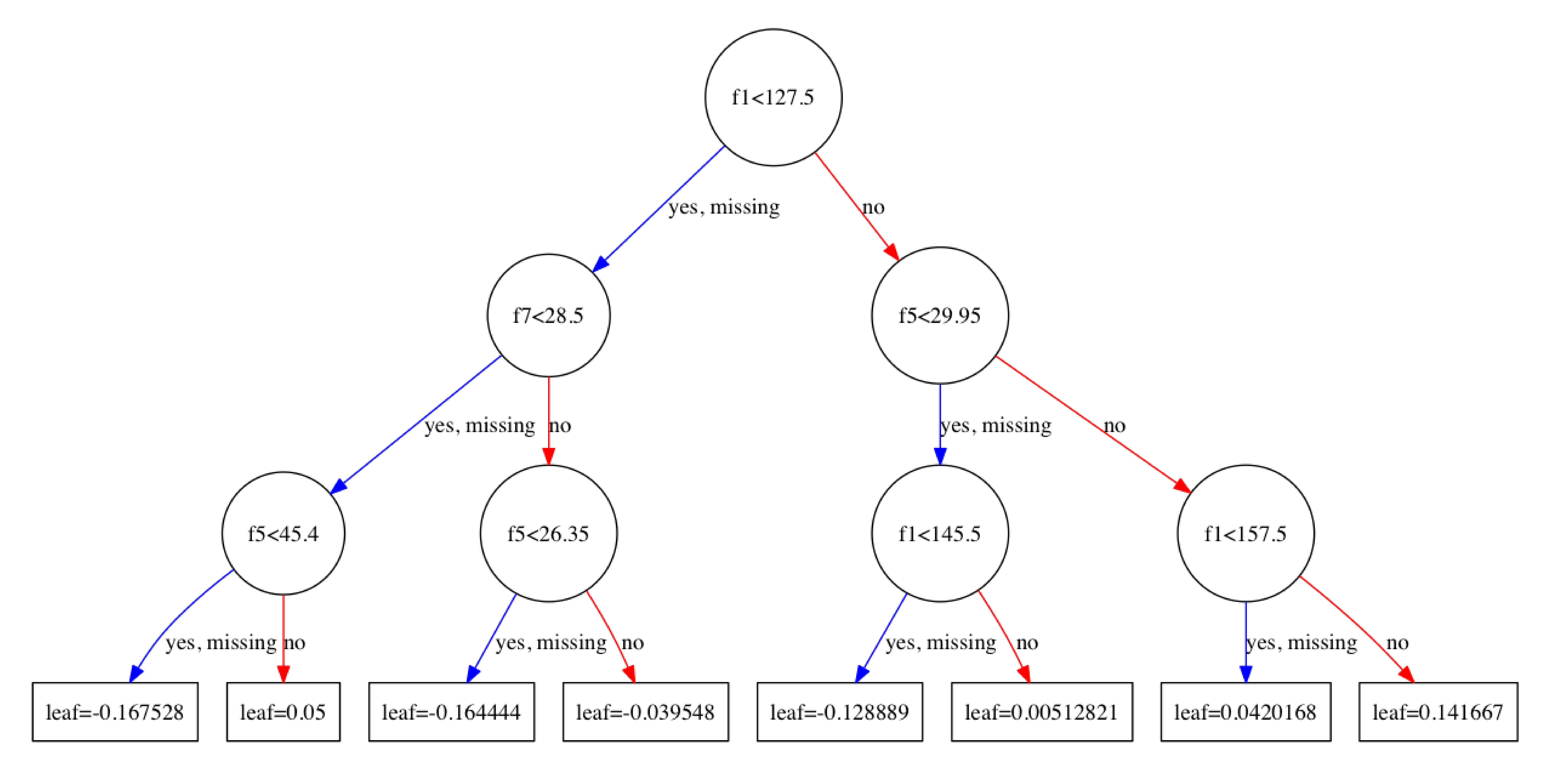
通过参数num_trees可以指定画哪棵树:plot_tree(model, num_trees=4)
画出来的有可能有点模糊,一个解决方案是设置图片的大小。1
plt.gcf().set_size_inches(100,100)
用plot_tree这个方法画的图可能有些简陋,对于不熟悉graphviz的人来说很难做定制化。笔者的一个想法是将XGBoost训练好的模型的以Json的格式输出,然后用前端的方法进行定制化。下面的开始的一些尝试:
首先获取正确格式的Json。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24#!/usr/bin/python
import xgboost as xgb
### simple example
# load file from text file, also binary buffer generated by xgboost
dtrain = xgb.DMatrix('data/agaricus.txt.train')
dtest = xgb.DMatrix('data/agaricus.txt.test')
# specify parameters via map, definition are same as c++ version
param = {'max_depth': 2, 'eta': 1, 'silent': 1, 'objective': 'binary:logistic'}
# specify validations set to watch performance
watchlist = [(dtest, 'eval'), (dtrain, 'train')]
num_round = 2
bst = xgb.train(param, dtrain, num_round, watchlist)
# this is prediction
preds = bst.predict(dtest)
labels = dtest.get_label()
print('error=%f' % (sum(1 for i in range(len(preds)) if int(preds[i] > 0.5) != labels[i]) / float(len(preds))))
ret = bst.get_dump(fmap='data/featmap.txt', dump_format='json')
with open('model.json', 'w') as outfile:
outfile.write('[' + ','.join(ret) + ']')输出的json如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75[
{
"nodeid": 0,
"depth": 0,
"split": "odor=pungent",
"yes": 2,
"no": 1,
"children": [
{
"nodeid": 1,
"depth": 1,
"split": "stalk-root=cup",
"yes": 4,
"no": 3,
"children": [
{
"nodeid": 3,
"leaf": 1.71218
},
{
"nodeid": 4,
"leaf": -1.70044
}
]
},
{
"nodeid": 2,
"depth": 1,
"split": "spore-print-color=orange",
"yes": 6,
"no": 5,
"children": [
{
"nodeid": 5,
"leaf": -1.94071
},
{
"nodeid": 6,
"leaf": 1.85965
}
]
}
]
},
{
"nodeid": 0,
"depth": 0,
"split": "stalk-root=missing",
"yes": 2,
"no": 1,
"children": [
{
"nodeid": 1,
"depth": 1,
"split": "odor=pungent",
"yes": 4,
"no": 3,
"children": [
{
"nodeid": 3,
"leaf": 0.784718
},
{
"nodeid": 4,
"leaf": -0.96853
}
]
},
{
"nodeid": 2,
"leaf": -6.23624
}
]
}
]根据Json画图
特征重要性
如何知道XGBoost模型每个特征的重要性呢?使用get_fscore函数。
get_fscore(fmap=’’)
Get feature importance of each feature.
Parameters: fmap (str (optional)) – The name of feature map file
get_score(fmap=’’, importance_type=’weight’)
Get feature importance of each feature. Importance type can be defined as:
‘weight’ - the number of times a feature is used to split the data across all trees. ‘gain’ - the average gain of the feature when it is used in trees ‘cover’ - the average coverage of the feature when it is used in trees
– 来自【4】
当importance_type设置为weight,重要性的衡量方式是特征在树上出现的次数。
预测
首先看一下预测的Python API1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17predict(data, output_margin=False, ntree_limit=0, pred_leaf=False, pred_contribs=False)
'''
Predict with data.
NOTE: This function is not thread safe.
For each booster object, predict can only be called from one thread. If you want to run prediction using multiple thread, call bst.copy() to make copies of model object and then call predict
Parameters:
data (DMatrix) – The dmatrix storing the input.
output_margin (bool) – Whether to output the raw untransformed margin value.
ntree_limit (int) – Limit number of trees in the prediction; defaults to 0 (use all trees).
pred_leaf (bool) – When this option is on, the output will be a matrix of (nsample, ntrees) with each record indicating the predicted leaf index of each sample in each tree. Note that the leaf index of a tree is unique per tree, so you may find leaf 1 in both tree 1 and tree 0.
pred_contribs (bool) – When this option is on, the output will be a matrix of (nsample, nfeats+1) with each record indicating the feature contributions of all trees. The sum of all feature contributions is equal to the prediction. Note that the bias is added as the final column, on top of the regular features.
Returns:
prediction
Return type:
numpy array
'''
细读几个参数:
pred_leaf=True会输出每条数据落在哪些叶子上pred_contribs=True会输出每条数据中每个特征对最后结果做的贡献。这些特征贡献值加起来就是预测值。
通过输出不同的信息可以对数据进行更细致的分析。